Navigating the 2024 Gmail and Yahoo Email Updates: Expert Insights for Marketers
- Mimi Glenn
- Feb 6, 2024
- 4 min read

It is February 2024, and major email service providers like Google and Yahoo are implementing new email delivery standards aimed at enhancing sender authentication and recipient preferences. These changes are designed to keep spoofed and unwanted emails out of our inboxes and prioritise legitimate and engaging content. As an industry expert in email deliverability, we want to guide you through these updates and provide essential information on the best email security best practices to ensure your emails continue to land in the inbox and, more importantly, stay there.
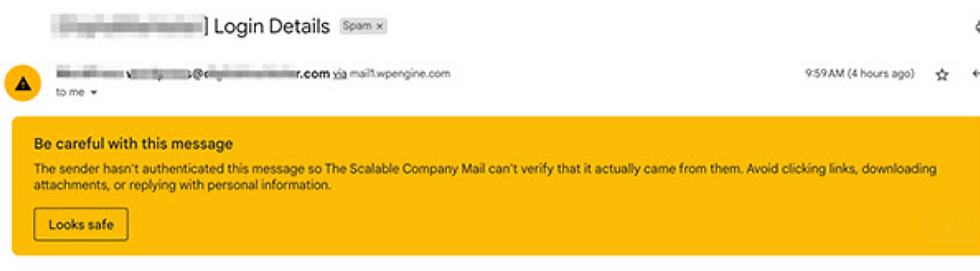
Understanding the Spam Algorithm Changes: Google and Yahoo's updated spam algorithms are set to reshape email deliverability. Successful email delivery now hinges on two crucial factors: IP address and domain sender reputation. Our focus today is on domain sender reputations, as these changes necessitate a custom email sender domain, the part that comes after the "@" symbol. To adapt to these changes effectively, you must be prepared for a "warming up" period to establish credibility with mailbox providers like Google and Yahoo.
The Domain Warming Process: Domain warming is the process of gradually building trust and credibility with mailbox providers. Here are some essential tips on warming up your sender domain:
Create a Timeline and Be Patient: Depending on the size of your email list, domain warming may take several weeks. Start by sending a limited number of emails per day and monitor performance closely.
Start with Your Best-Performing Email and Audience: Engagement is a key factor in deliverability. Begin the warmup process with your most engaged audience, using emails with historically high open and click-through rates.
Maintain Consistency: Avoid sending emails sporadically. Consistency is crucial, so establish a regular sending schedule to build trust with mailbox providers.
Monitor Performance and Adjust: Continuously monitor delivery rates and engagement metrics. If you observe low performance, be ready to reduce the number of emails sent.
Additional Tips for Success and Less Stress:
Clean your email list before beginning the warmup process.
Develop a schedule for sending top-performing emails.
Keep transactional emails running alongside promotional messages.
Utilise monitoring tools like Google Postmaster Tools to analyse email performance.
Conclusion: As Gmail and Yahoo enforce stricter email sender requirements, it is crucial for marketers to adapt and stay ahead of these changes. Effective email domain warming is essential to maintain a positive sender reputation and ensure successful email campaigns. By following best practices, monitoring performance, and being proactive, you can navigate the 2024 email updates with confidence and continue delivering engaging content to your audience.
We understand that these changes can be challenging, and some email software platforms such as Mailerlite are butting heads with google, but we are here to help you through the transition. If you work with an email platform that has specific challenges we recommend taking a cooling off period whilst Google/Yahoo and your provider make friends again.
We are here to provide solutions that will enhance your email marketing strategy and achieve better results. Gmail and Yahoo's updates are an opportunity to refine your email marketing approach and create more meaningful connections with your subscribers.
Read on if you want to know more about DMARC set up (marketing managers etc)
To ensure the security and authenticity of your domain, it is essential to configure SPF (Sender Policy Framework) and DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) records in your domain's DNS settings. However, with the recent updates from Google and Yahoo taking effect in February 2024, organisations sending 5,000+ emails daily must take another step to bolster their email security by implementing DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance).
What Exactly Is DMARC?
DMARC is a powerful email authentication, policy, and reporting protocol that requires a TXT record in your domain's DNS settings. It plays a vital role in validating the origin of emails by scrutinising the sender's IP address. Essentially, DMARC aims to prevent direct domain spoofing through DKIM and SPF identifier alignment. If an email message claims to be from your domain but fails the DKIM and/or SPF checks, DMARC provides instructions to the recipients' email servers on how to handle it. This helps differentiate fraudulent emails from legitimate ones, mitigating the risk of scams.
Implementing DMARC: A Few Key Steps
If your business frequently sends a high volume of emails (around 5,000+), if your domain faces a high risk of spoofing, or if you want to monitor outgoing emails sent on your domain's behalf, setting up a DMARC policy is highly recommended. To ensure a seamless implementation and minimise any potential negative impact on your email delivery, we advise seeking assistance from DMARC consulting companies.
Understanding Identifier Alignment
DMARC ensures the alignment of domains to verify the authenticity of the sender. It checks whether the domain in the Header/From field (the sender's email) matches one or both domains specified in the DKIM or SPF record. Alignment is crucial:
Strict Alignment: The domains must be an exact match.
Relaxed Alignment: The domains can have different subdomains of the same root domain.
Unveiling DMARC Tags
A DMARC record comprises several tags, some mandatory and others optional. Here is an example of a basic DMARC record:
cssCopy codev=DMARC1; p=none; rua=mailto:dmarc@yourdomain.com
Mandatory Tags:
v: Identifies the record as DMARC (always DMARC1).
p: Indicates the chosen policy, governing how email mailbox providers should handle emails failing DMARC authentication.
p=none: A monitoring policy, allowing you to track emails sent on your domain's behalf.
p=quarantine: Directs emails failing DMARC checks to recipients' junk or spam folders, while also enabling tracking.
p=reject: Instructs email servers to reject emails that fail DMARC checks, resulting in bounces and non-delivery, alongside comprehensive tracking.
Incorporating DMARC into your email security strategy is an essential step in safeguarding your domain's integrity and enhancing email authentication. With the right policies and alignment, you can ensure that your emails are delivered securely and reliably. If you have any questions or need assistance with implementing DMARC, don't hesitate to reach out to us.
Don't forget we are here to help you navigate these important changes in the email landscape.




Comments